On 23JAN2020, the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) and Kratos Defense & Security Solutions (Kratos) conducted a successful 4th flight of the XQ-58A low-cost, long-range attack ‘drone’ (Low Cost Attritable Aircraft Technology), over the U.S. Army’s Yuma Proving Grounds (YPG) in Arizona.
Length 9.14m, wingspan 8.2m, dry weight 1134kg, maximum take-off weight 2722kg. Internal bomb-bay with two GBU-39 bombs, wings will have hard points for weapons, maximum payload of 544kg. Turbofan engine producing 2000lb thrust.
“The Valkyrie is a remarkable accomplishment requiring a highly collaborative approach to meet the program’s performance and cost objectives, all while achieving first flight in 30 months.”-Doug Szczublewski, AFRL, November 2019
Apparently one of the innovations of the XQ-58A team is the creation of an 11-feet long air intake duct made with resins.
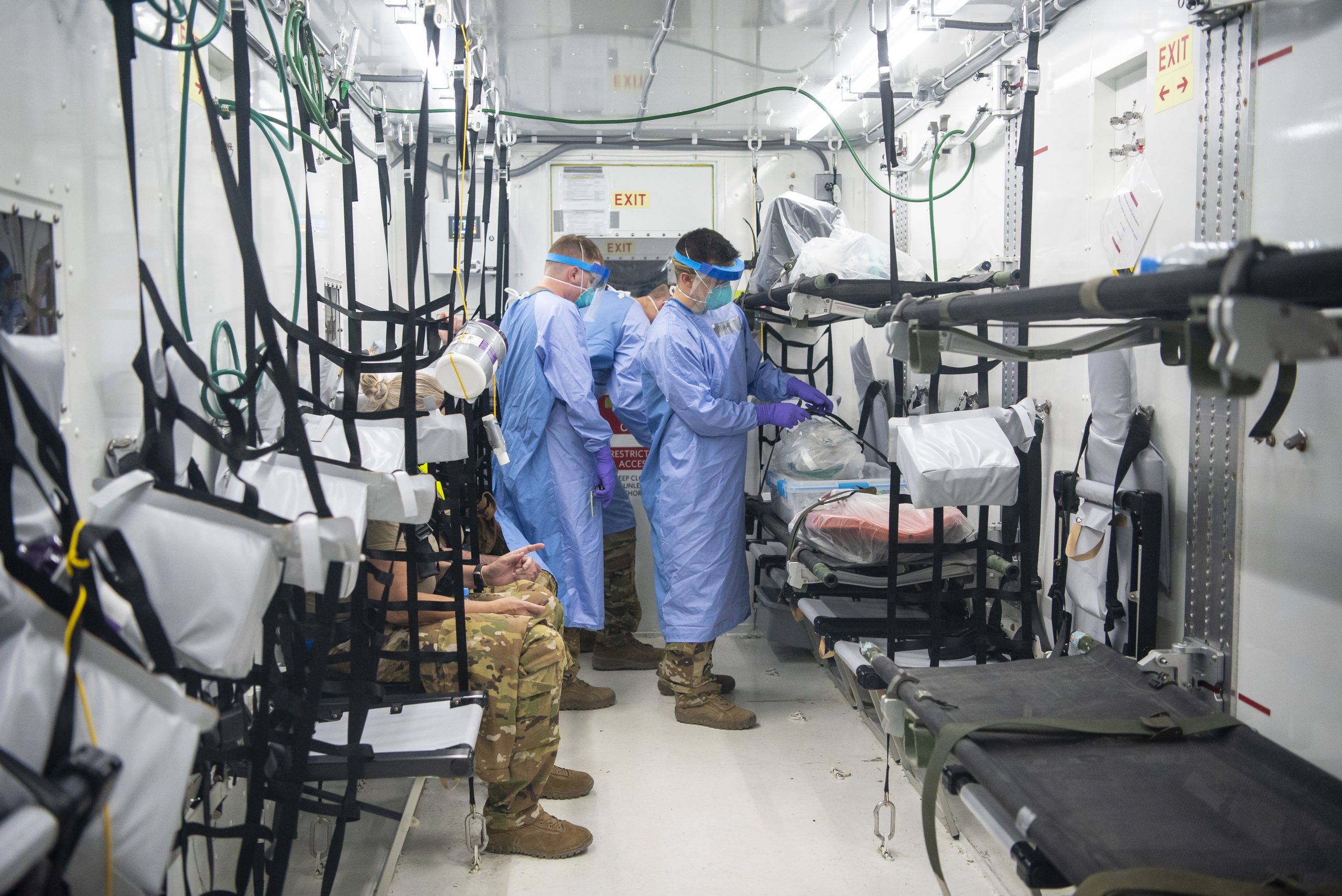
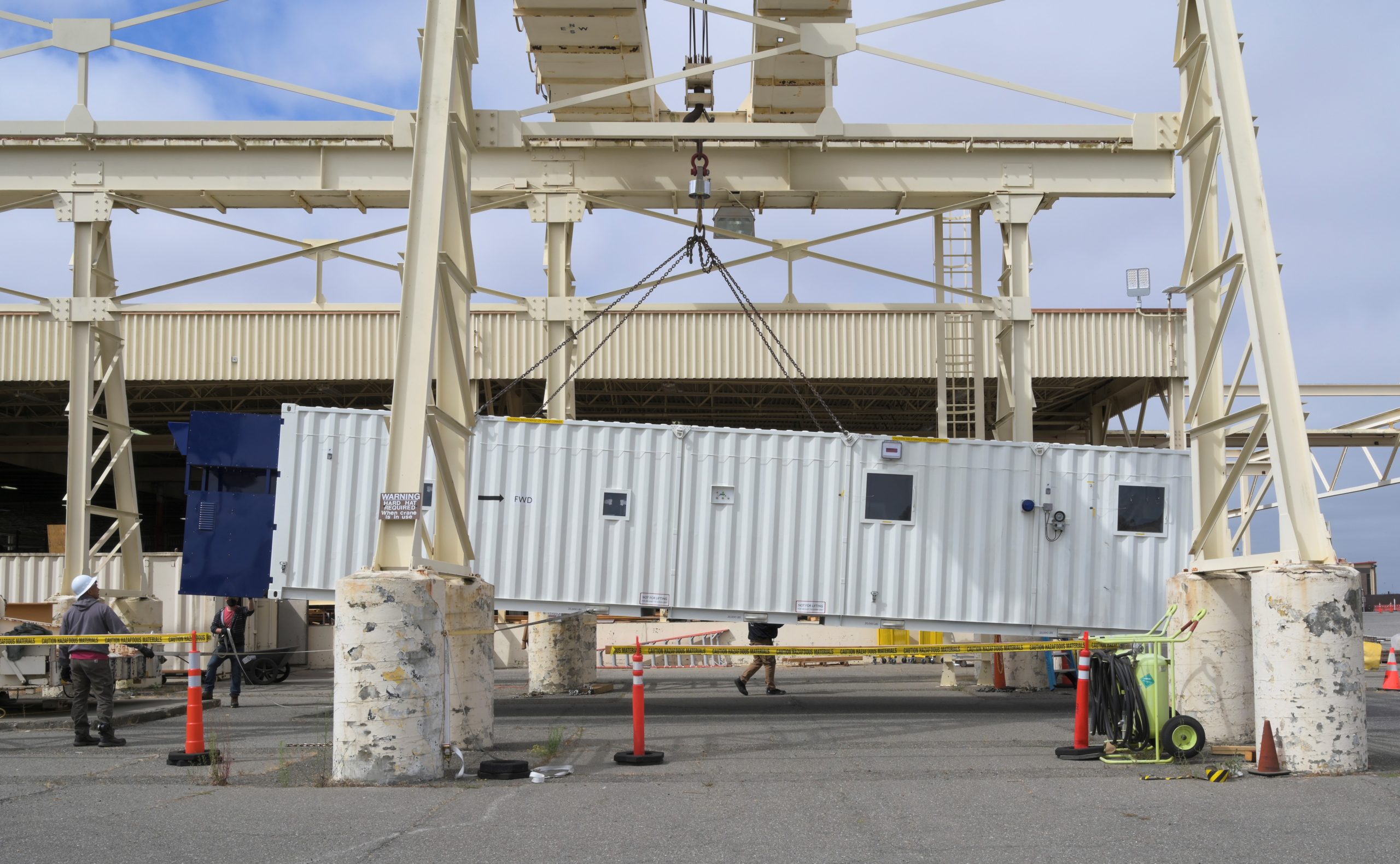
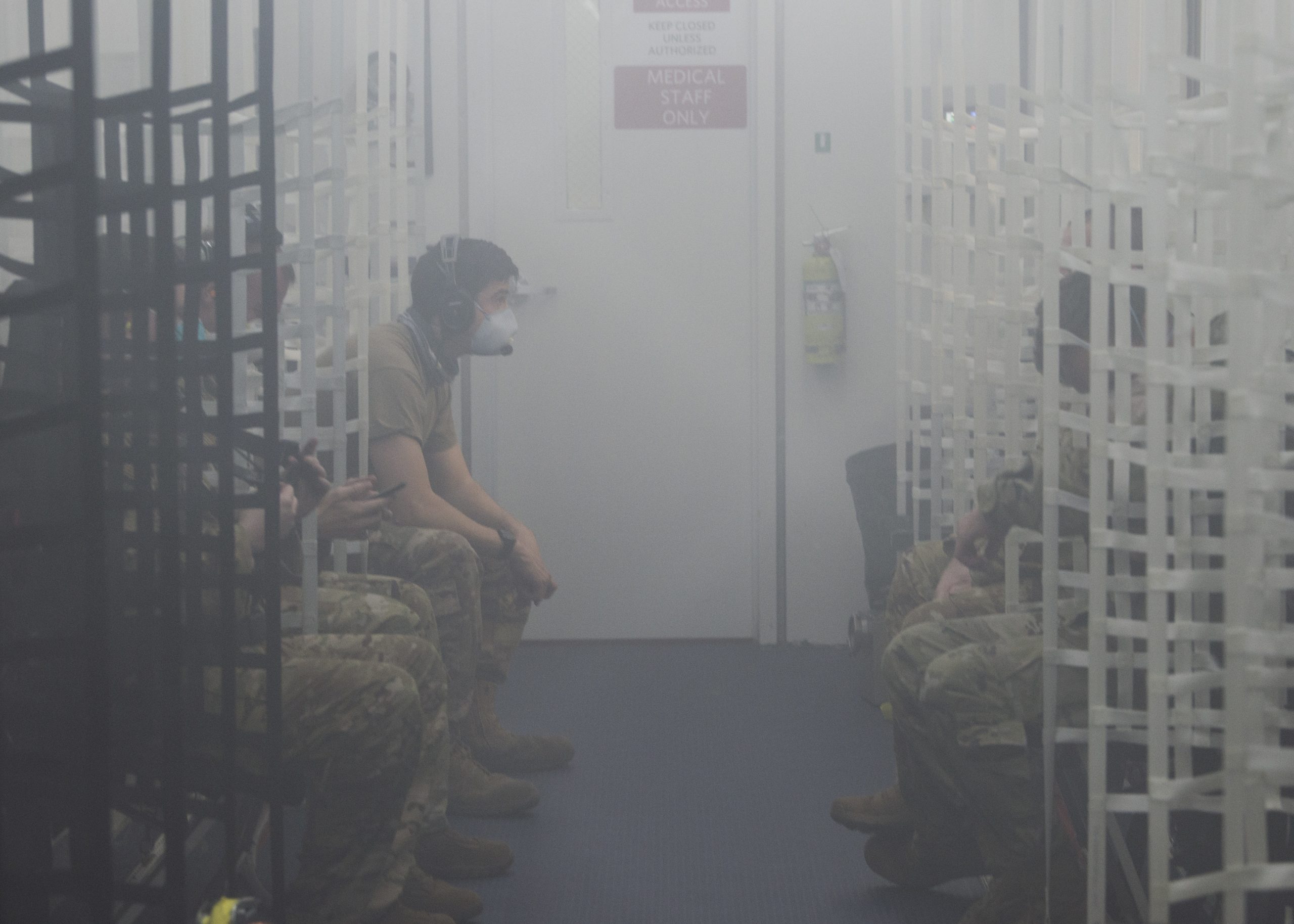
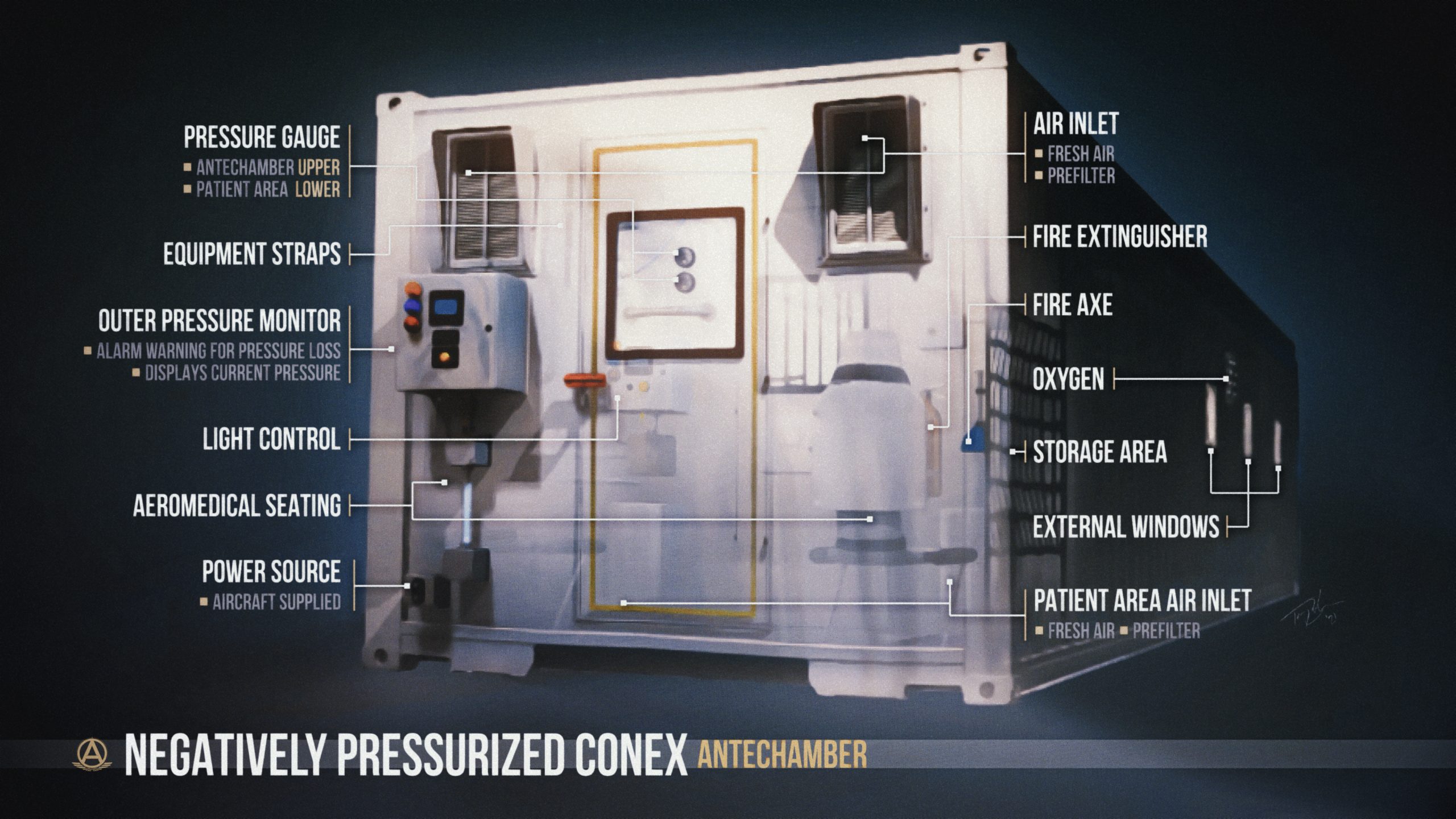
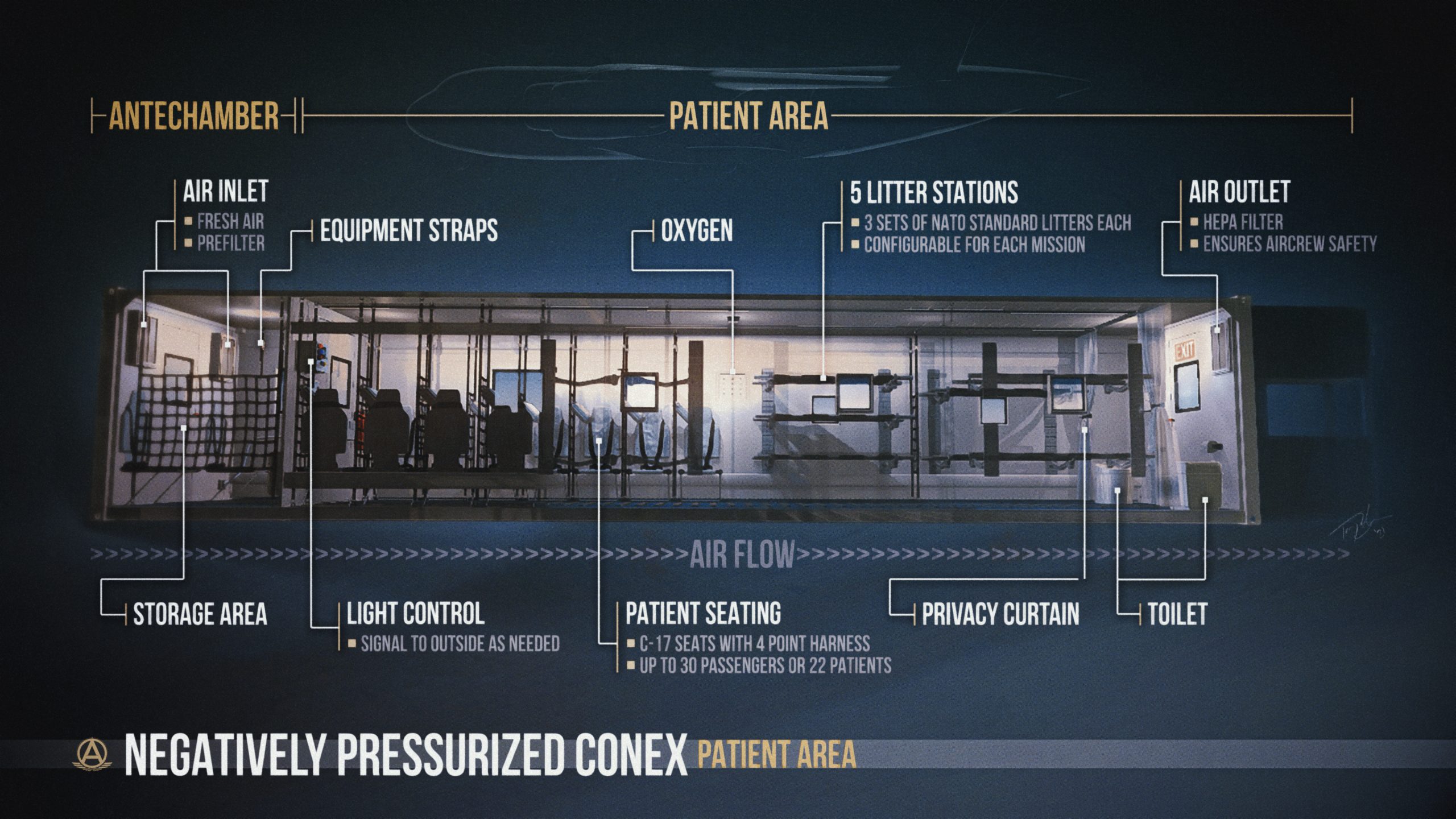
Kratos representatives say the XQ-58A and its launcher can fit inside a standard Conex shipping container. (USAF finds new use for Conex: NEGATIVE PRESSURE FLYING HOSPITALS?)
Short silent video from the first flight, 05MAR2019, over YPG:
In October 2019 the new Valkyrie crashed while landing, high-speed winds and failure of the ‘recovery system’ being blamed. Supposedly it does not need a paved runway to land on (using parachutes and airbags), and can conduct a wide-range of missions (surveillance, reconnaissance and long-range combat) at far less the cost of current unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV, aka drones).
It is also hoped that it can act as an unmanned wingman for piloted, and super expensive, F-35 aircraft (by encrypted data link). The USAF has been very quiet about this new aircraft, so far releasing only a couple of pics and the short silent video. Despite 2019’s crash, production has already started: “We are leaning forward here, ahead of the expected contract awards as we are highly confident that receipt of initial Valkyrie production contracts is not if, but when….”-Eric DeMarco, Kratos
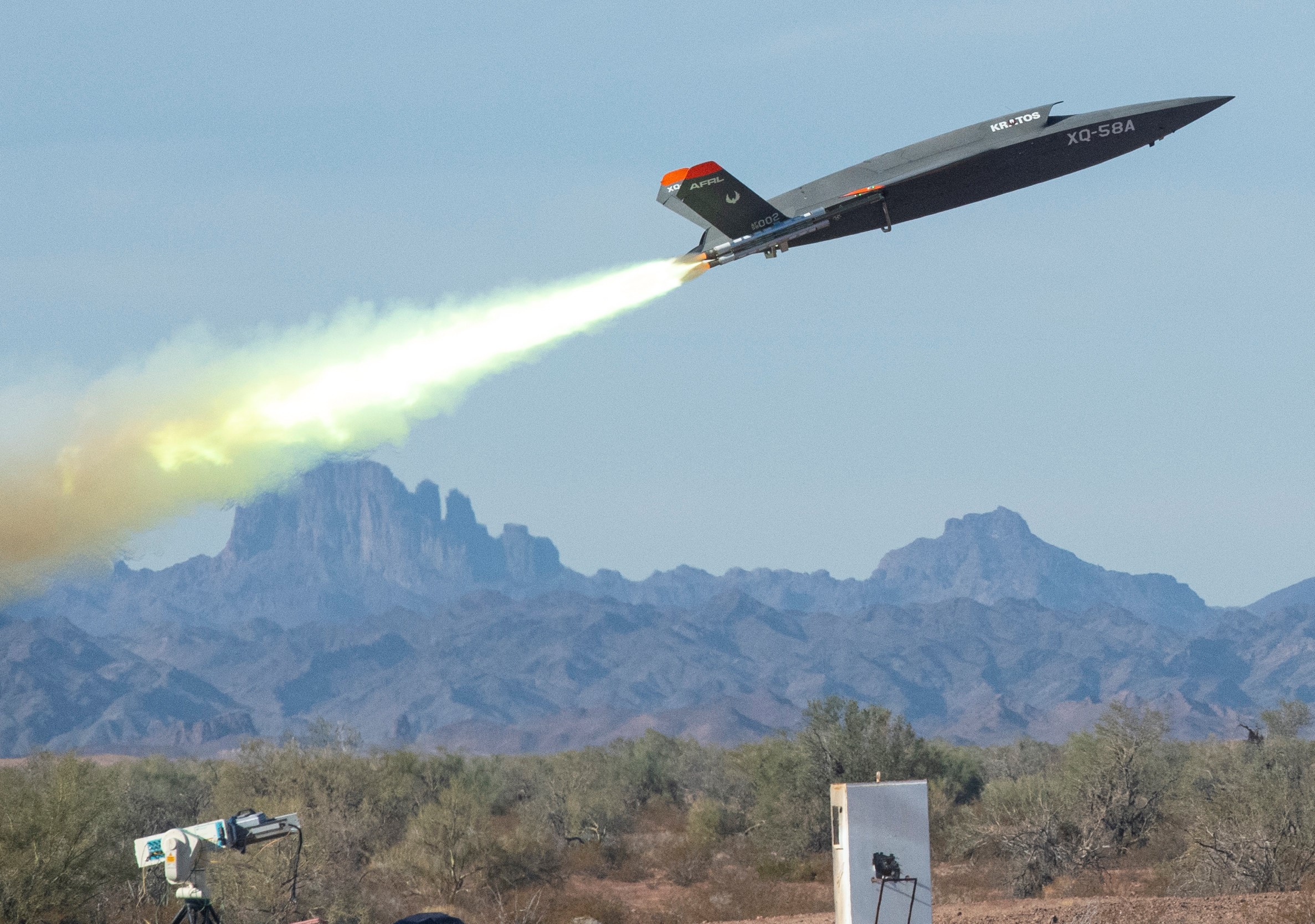

U.S. Army Yuma Proving Ground, Arizona, 09DEC2020. U.S. Air Force photo by Staff Sergeant Joshua King.
USAF video, from December 2020, admitting that the XQ-58A was a failure:
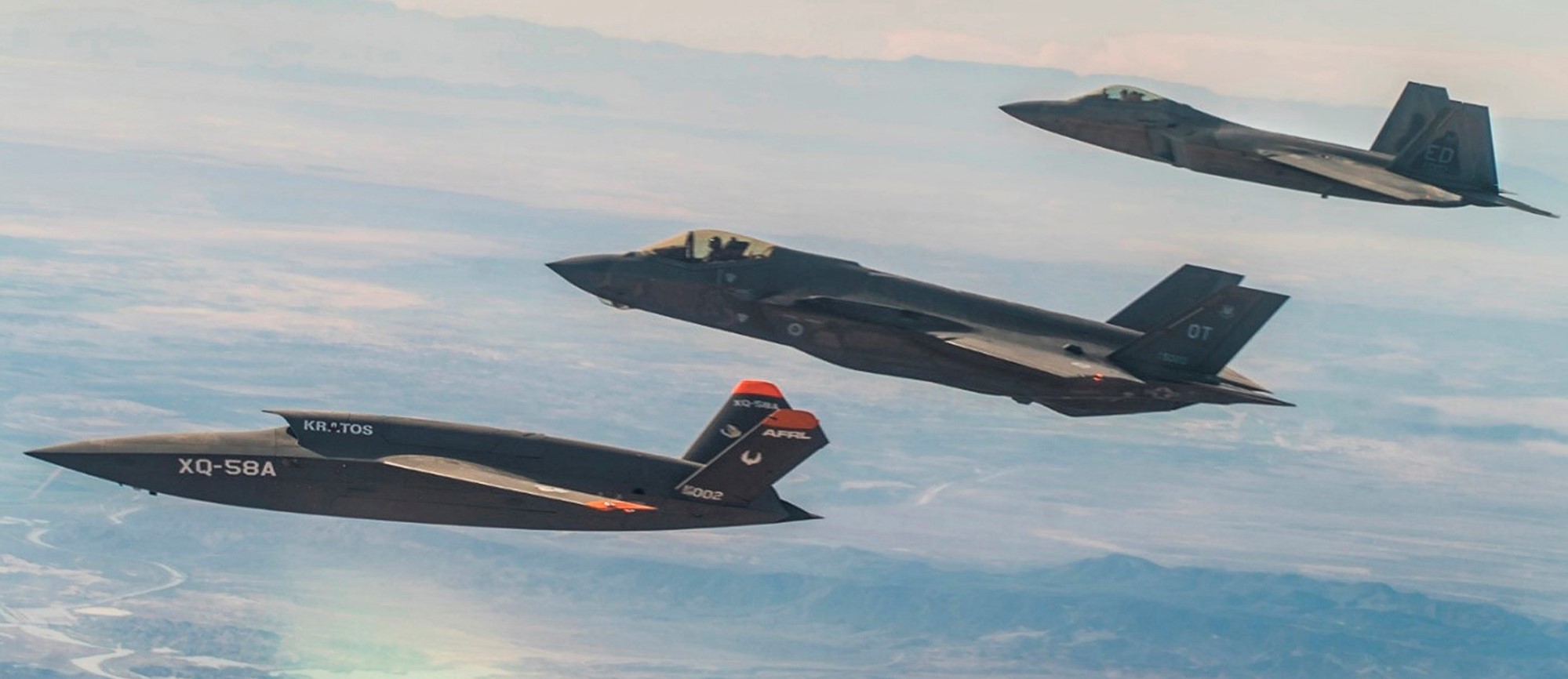

During the 09DEC2020 test, the F-35 Lightning-2, and an F-22 Raptor, were supposed to be able to ‘communicate’ with their unmanned wingman, the XQ-58A. It didn’t work. Photo via Air Force Magazine.
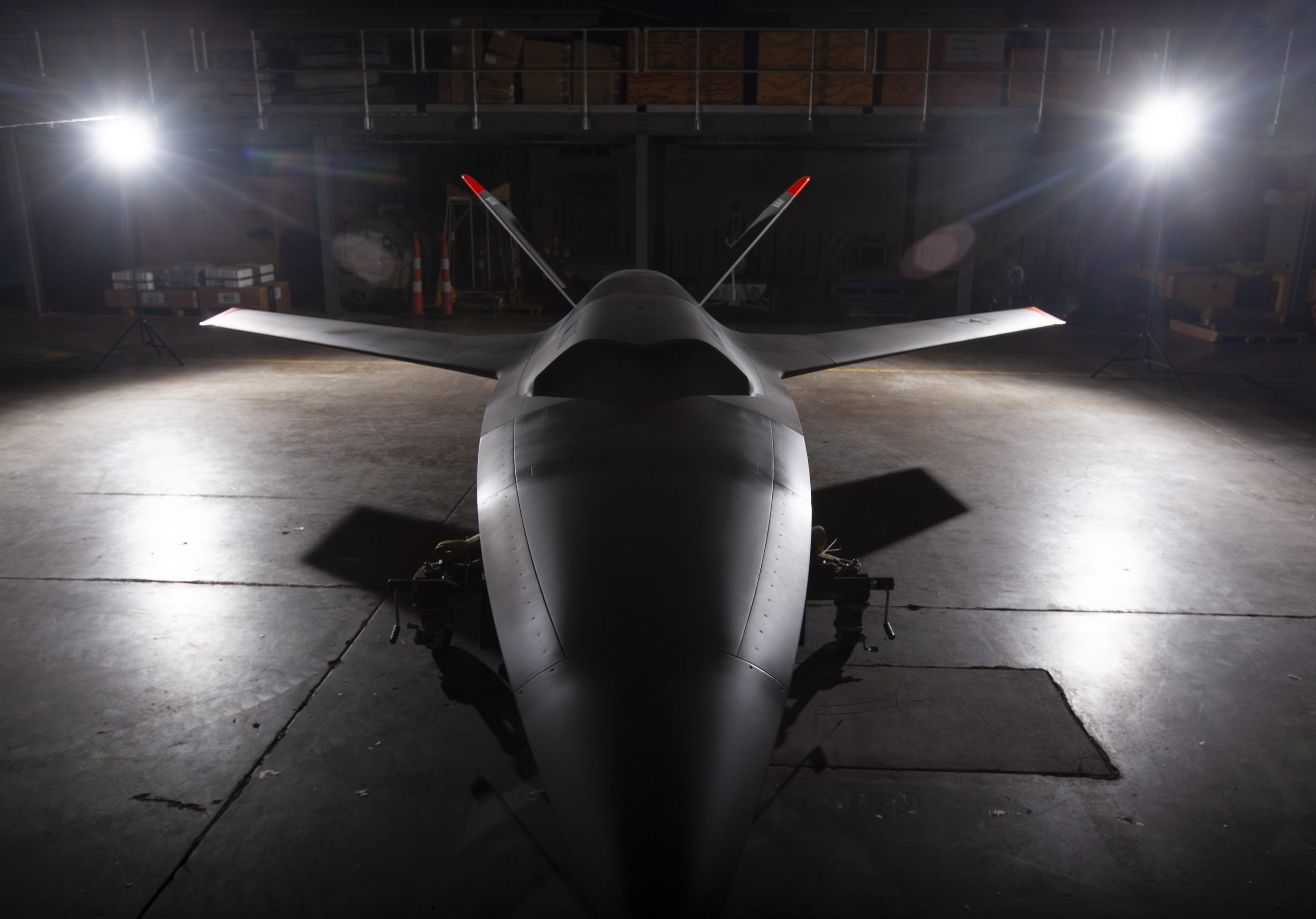

In July 2021, the ‘advanced’ XQ-58 Valkyrie suddenly became a museum piece in the National Museum of the U.S. Air Force. USAF photo by Ty Greenlees.
The company that made the XQ-58A (with taxpayer funding) still lists it as one of their available products. According to a July 2022 U.S. Air Force Magazine article, two more XQ-58A drones are being used in the Skyborg program (TERMINATOR: NEW F-16/X-62 SKYBORG), interestingly the decision to do so came at the end of 2020.
Vehicle I-D: XB-70A VALKYRIE





 High Mach speed stripped the then standard thickness paint from the aircraft.
High Mach speed stripped the then standard thickness paint from the aircraft.
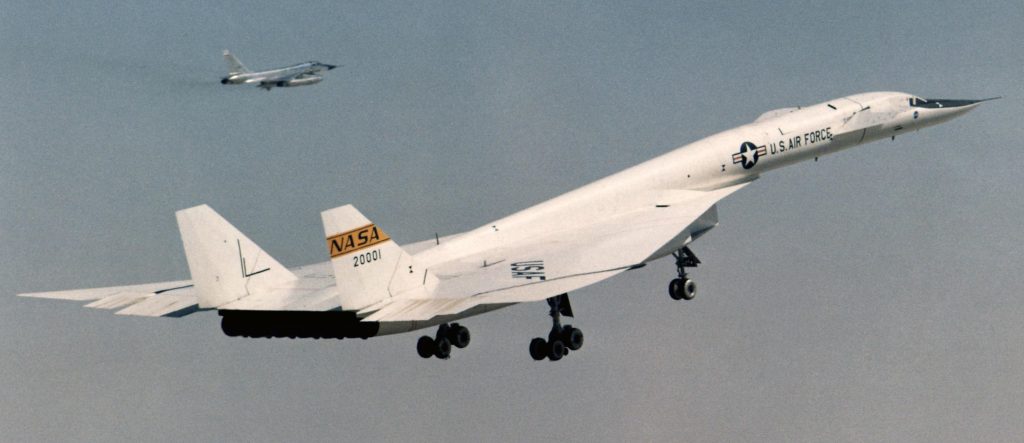
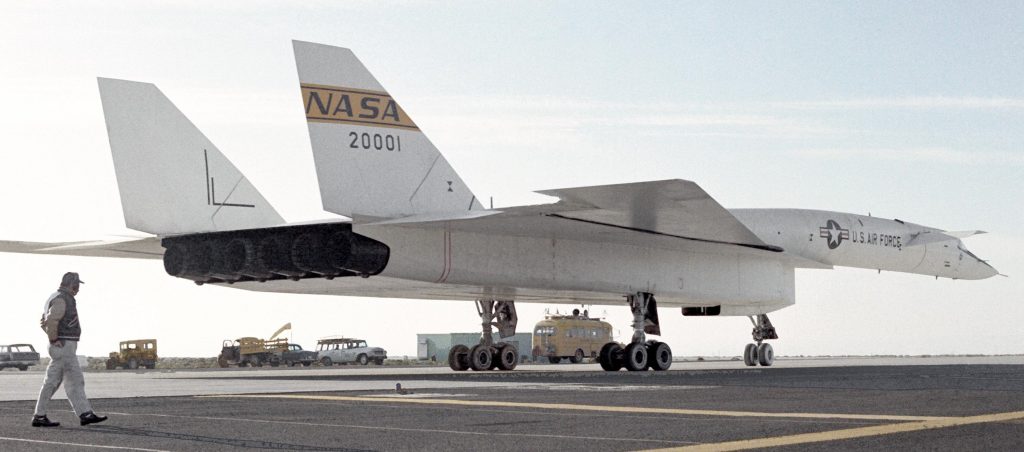











 Valkyrie 20001 after arrival at Wright Patterson Air Force Base, February 1969.
Valkyrie 20001 after arrival at Wright Patterson Air Force Base, February 1969. Being flown down the road to its retirement home known as a museum, 1971.
Being flown down the road to its retirement home known as a museum, 1971.
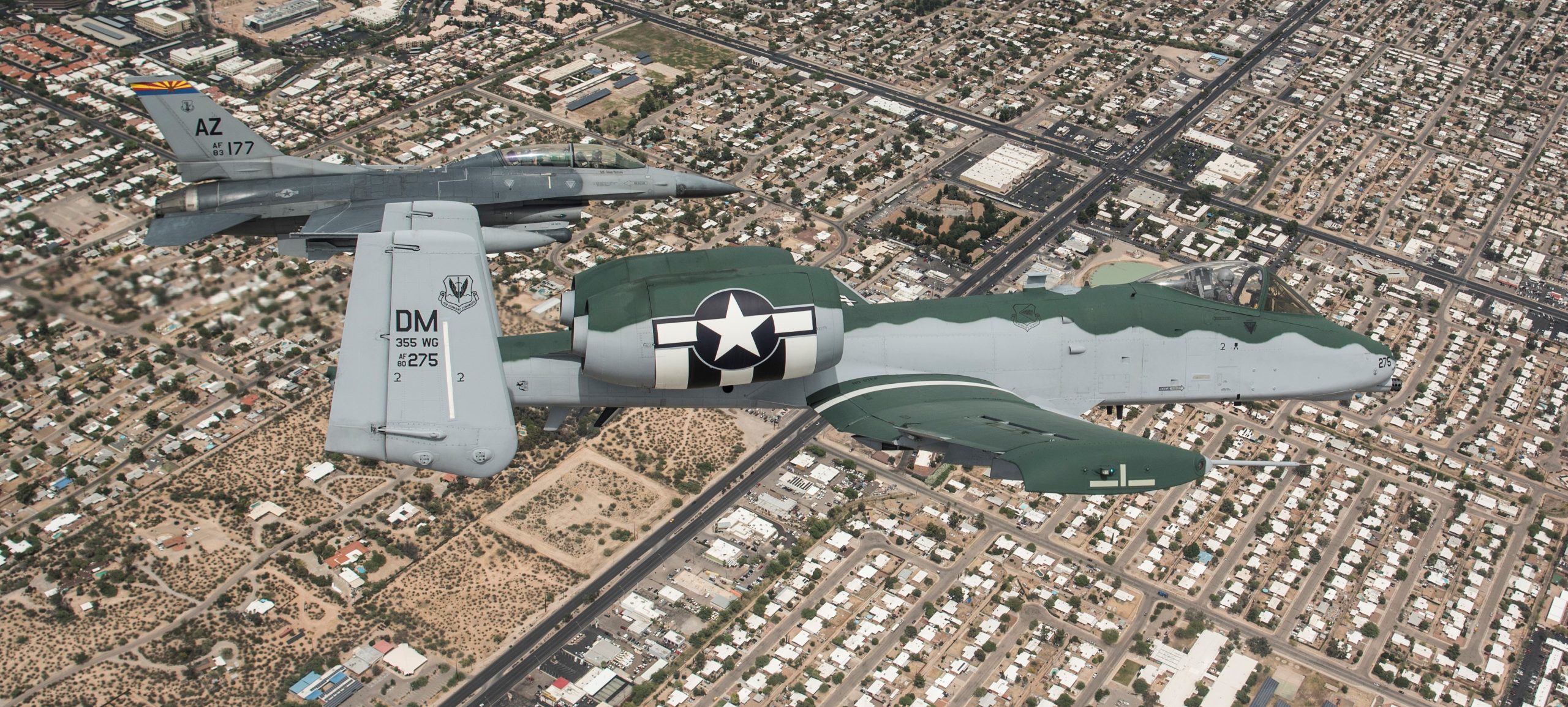
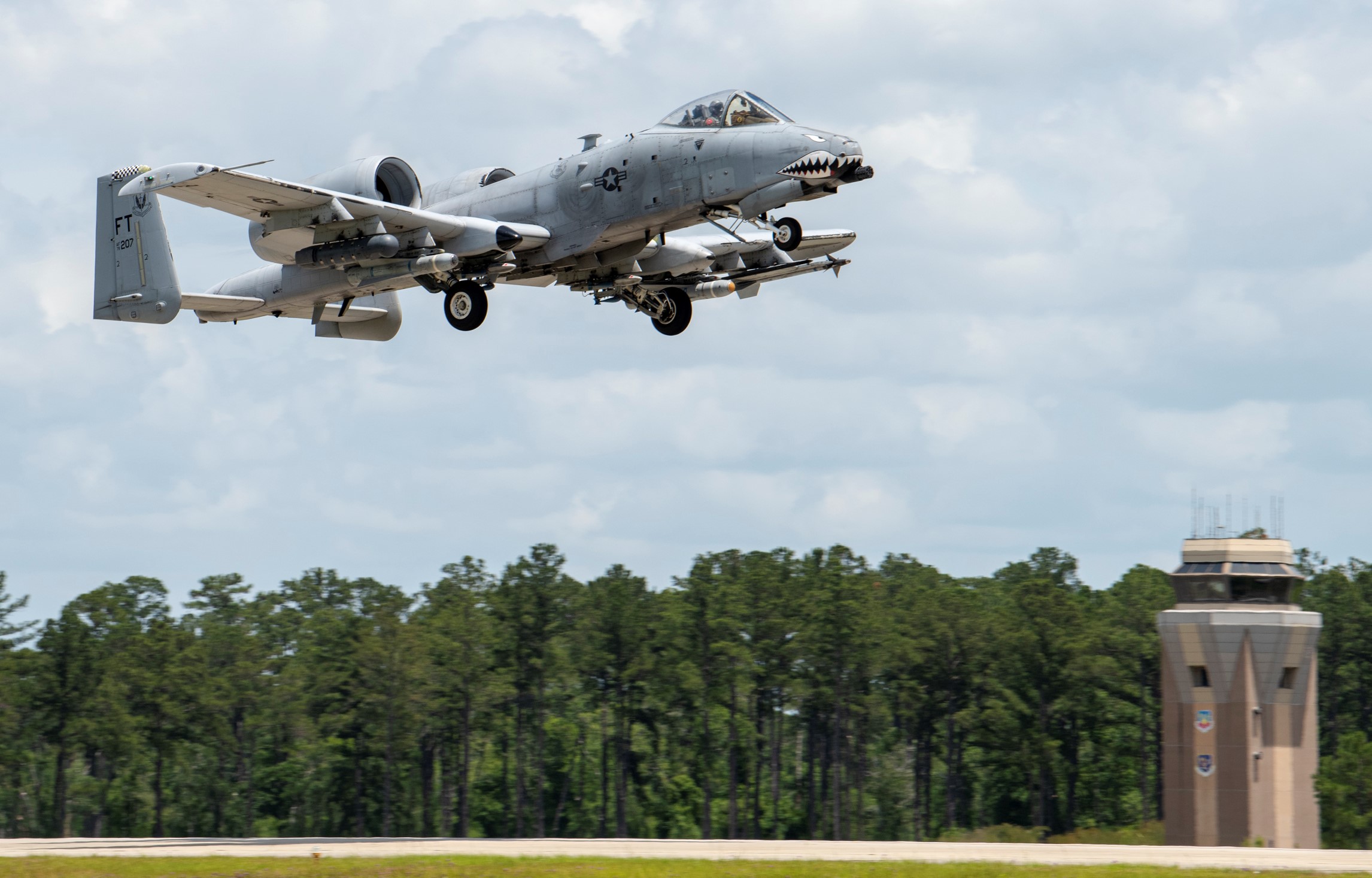
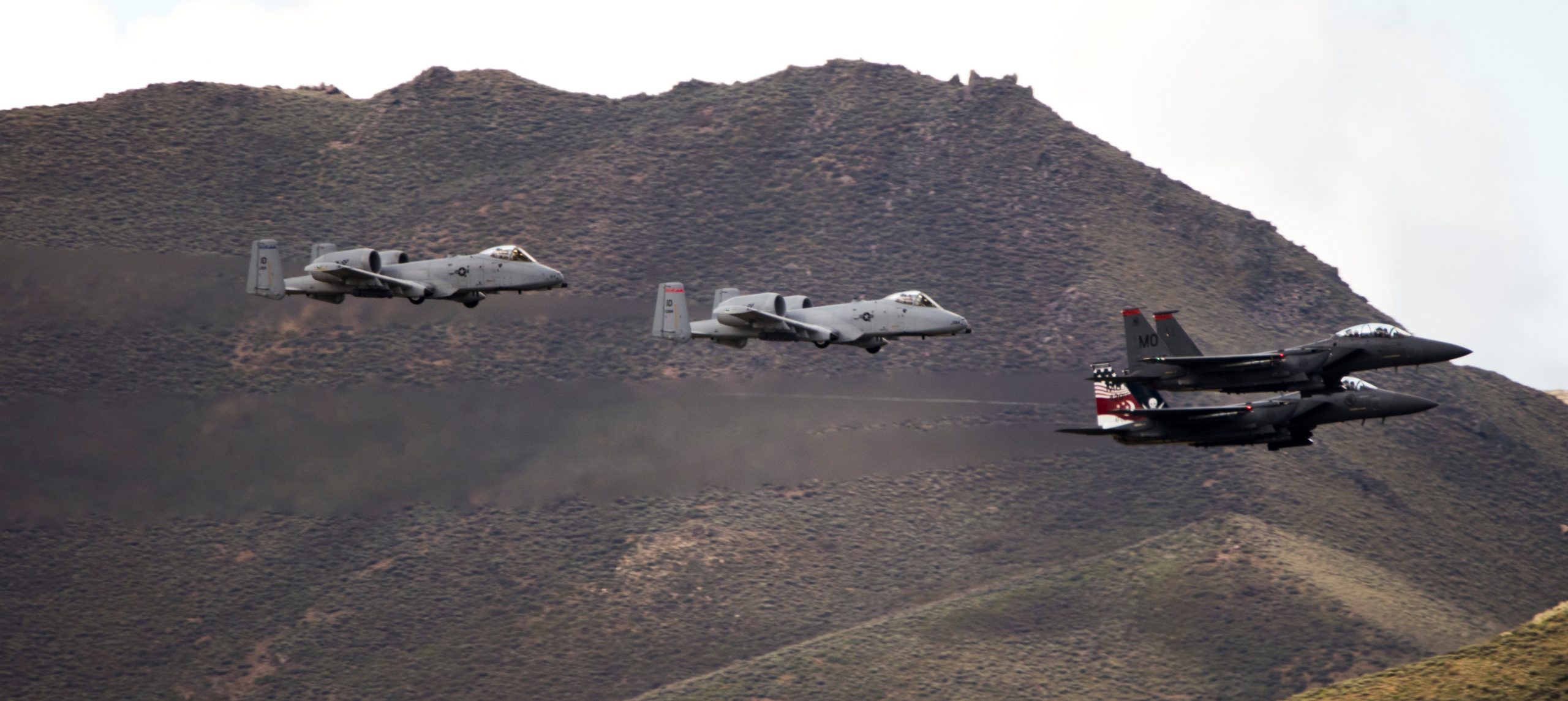













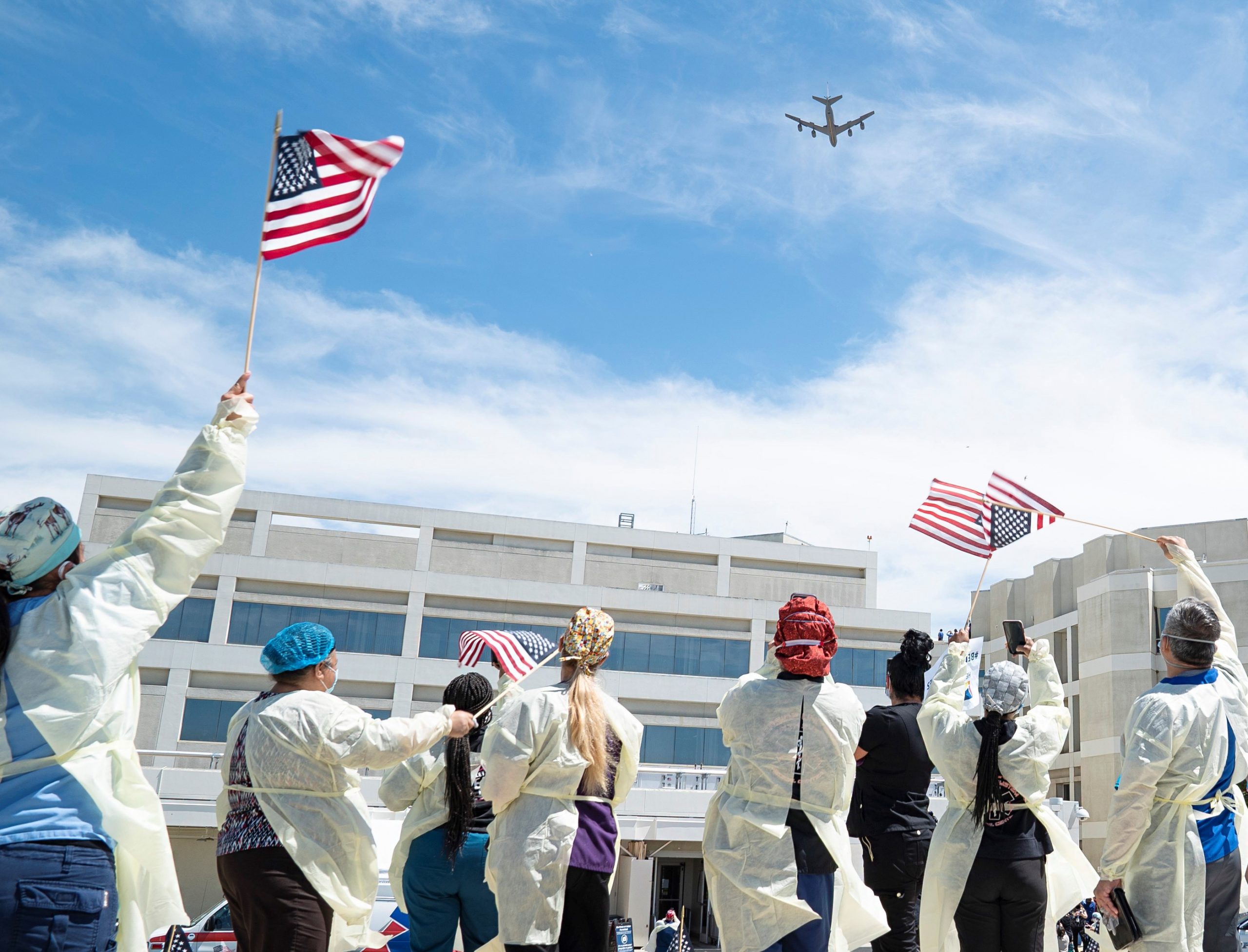
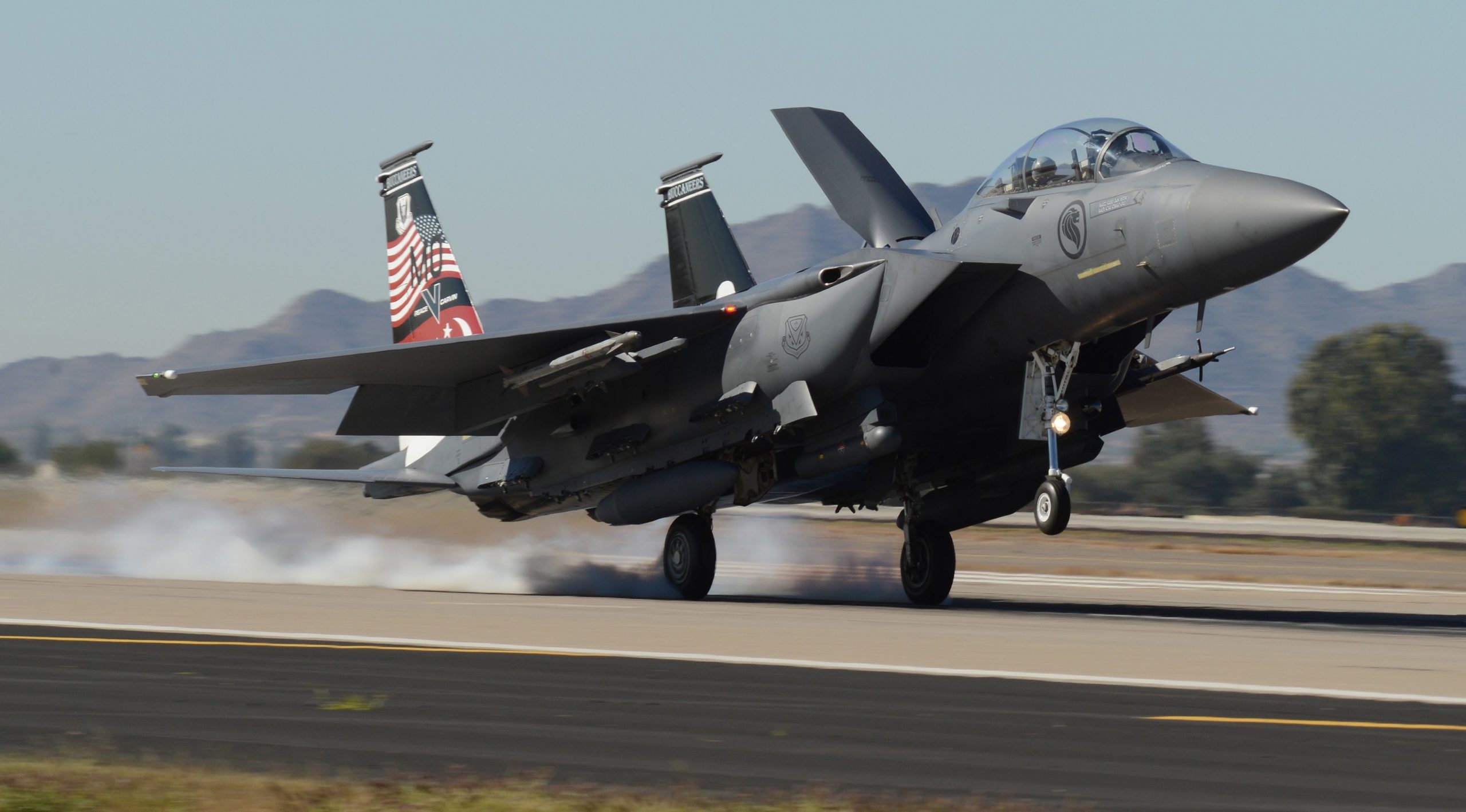
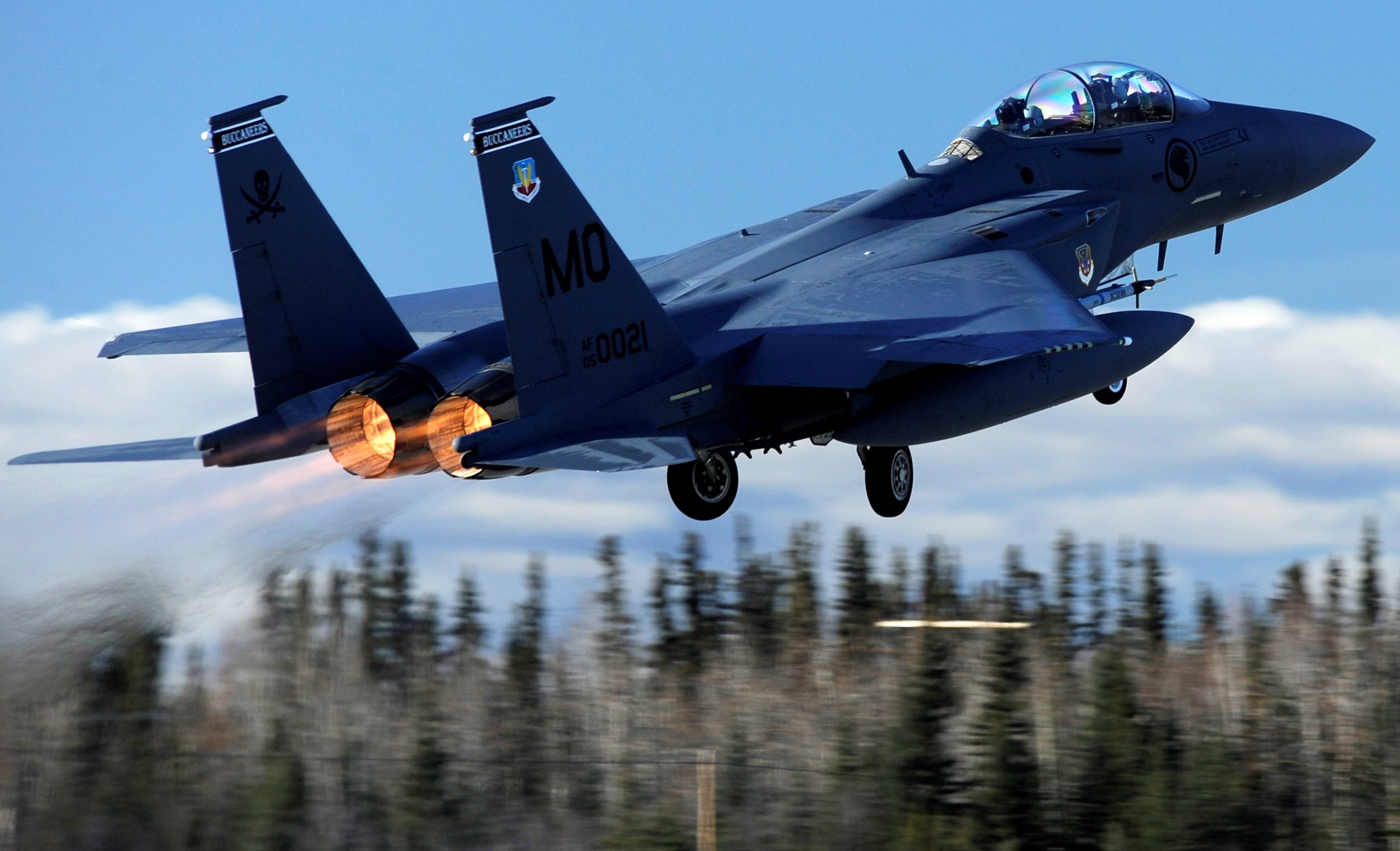
 Indiana Air National Guard 122nd Fighter Wing over Terre Haute, 02MAY2020.
Indiana Air National Guard 122nd Fighter Wing over Terre Haute, 02MAY2020. 122nd Fighter Wing, Indiana Air National Guard, over Fort Wayne on 13MAY2020.
122nd Fighter Wing, Indiana Air National Guard, over Fort Wayne on 13MAY2020. Maryland Air National Guard 175th Wing A-10Cs over local hospitals, 08MAY2020.
Maryland Air National Guard 175th Wing A-10Cs over local hospitals, 08MAY2020.
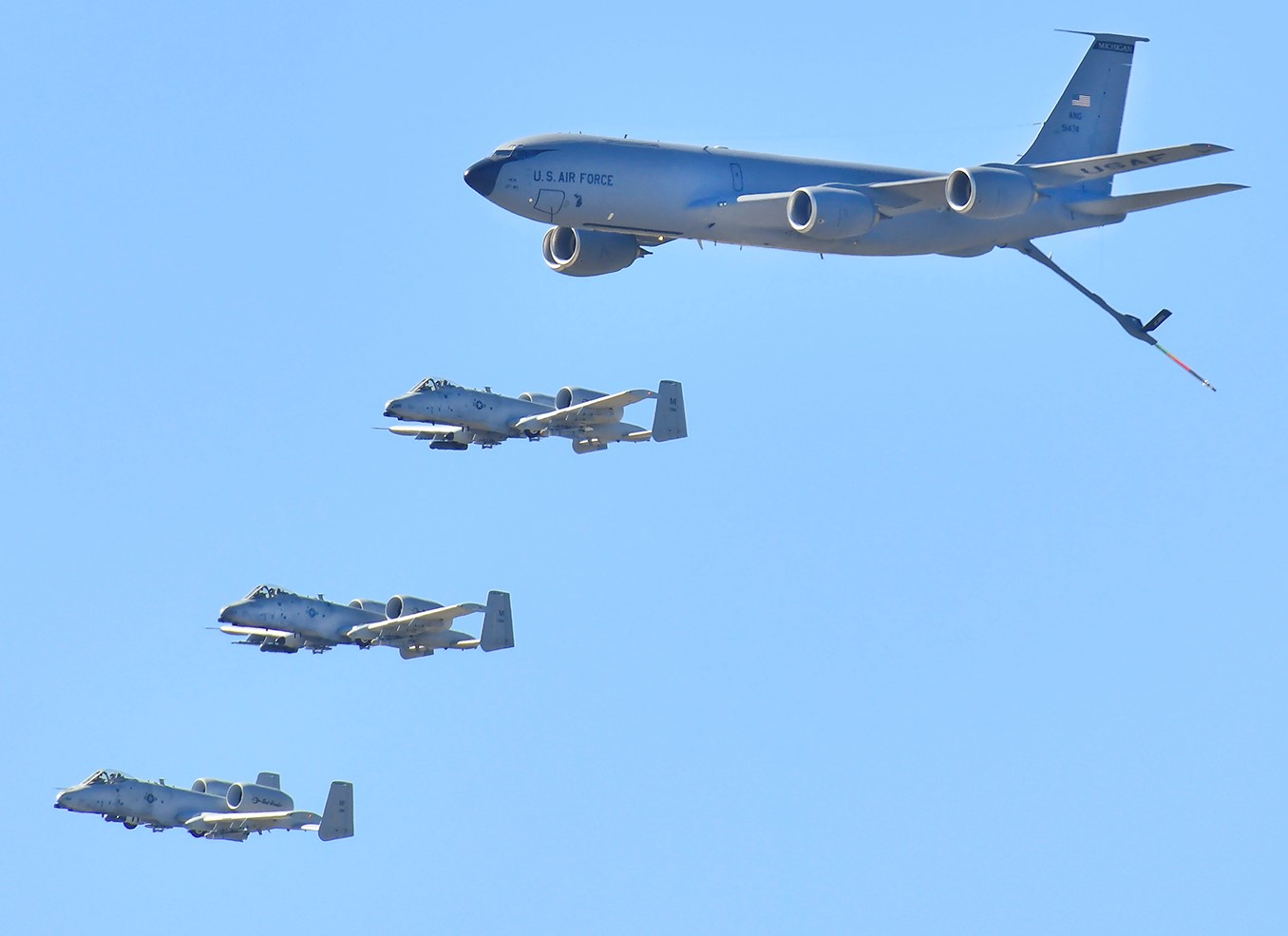








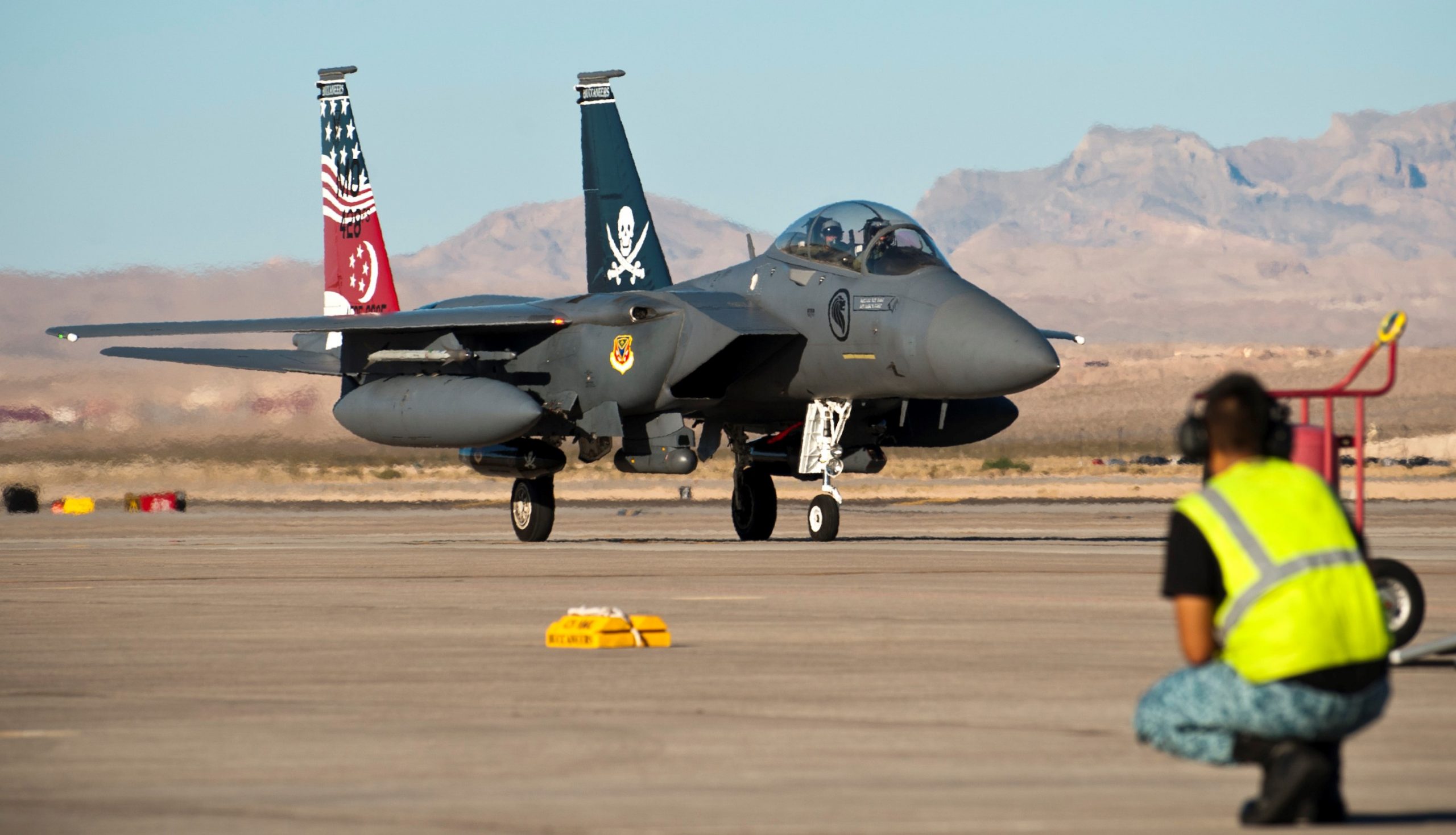
 A KC-135 leads a pack of F-16s and F-35s on a Air Force Salutes flight over Arizona, 01MAY2020. At least 15 aircraft were involved.
A KC-135 leads a pack of F-16s and F-35s on a Air Force Salutes flight over Arizona, 01MAY2020. At least 15 aircraft were involved.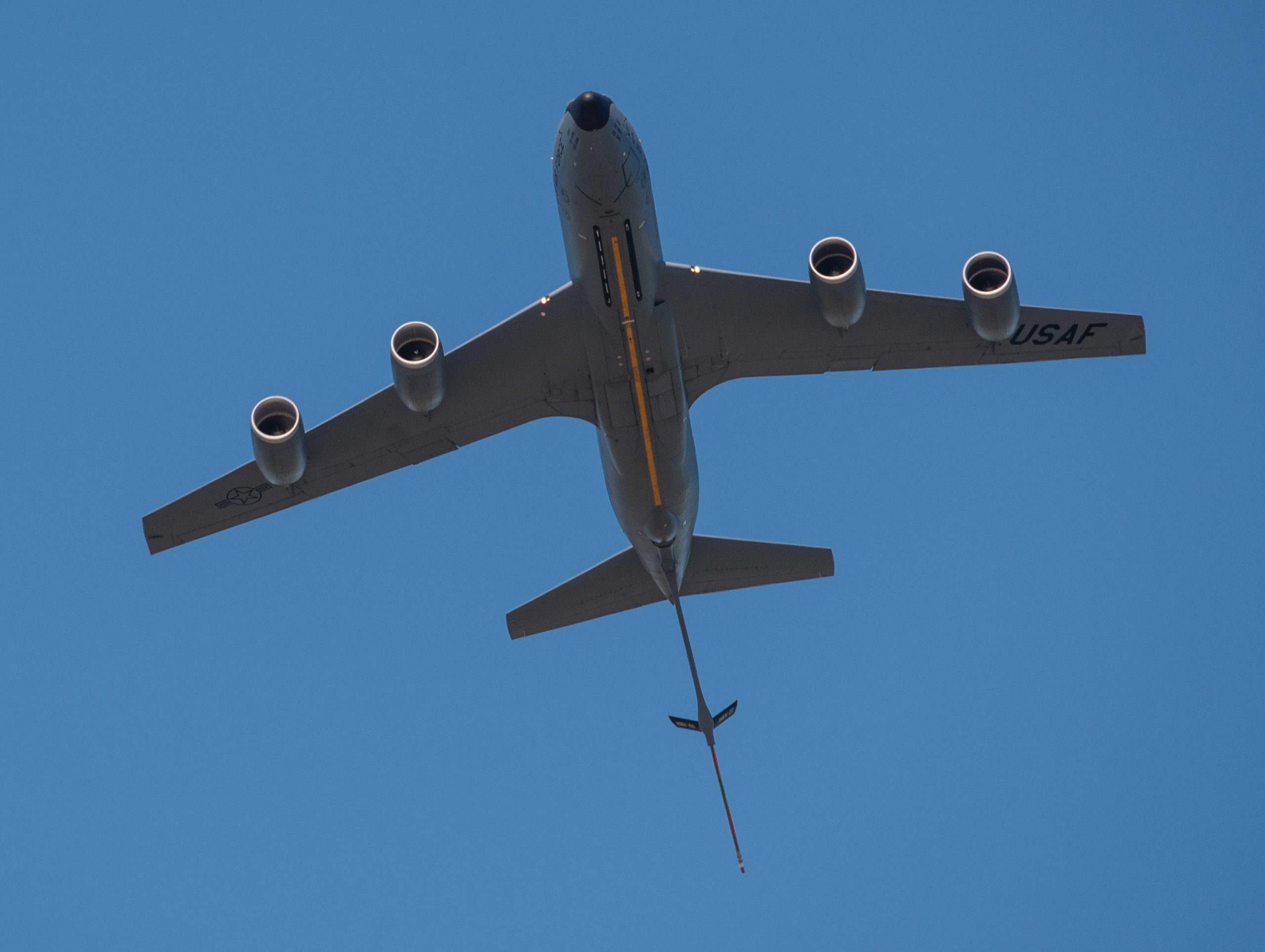


 The crew of a Michigan Air National Guard 127th Wing KC-135 just before taking off for a Michigan Strong flyover, 13MAY2020.
The crew of a Michigan Air National Guard 127th Wing KC-135 just before taking off for a Michigan Strong flyover, 13MAY2020. KC-135R from the 914th Air Refueling Wing, Niagara Falls Air Reserve Station, in formation with F-35s from the 158th Fighter Wing, Vermont Air National Guard Base, 12MAY2020.
KC-135R from the 914th Air Refueling Wing, Niagara Falls Air Reserve Station, in formation with F-35s from the 158th Fighter Wing, Vermont Air National Guard Base, 12MAY2020. Ohio Air National Guard KC-135 flies with an F-16 during Operation American Resolve, 13MAY2020.
Ohio Air National Guard KC-135 flies with an F-16 during Operation American Resolve, 13MAY2020. Tail boom of 134th Air Refueling Wing, Tennessee Air National Guard, 12MAY2020.
Tail boom of 134th Air Refueling Wing, Tennessee Air National Guard, 12MAY2020.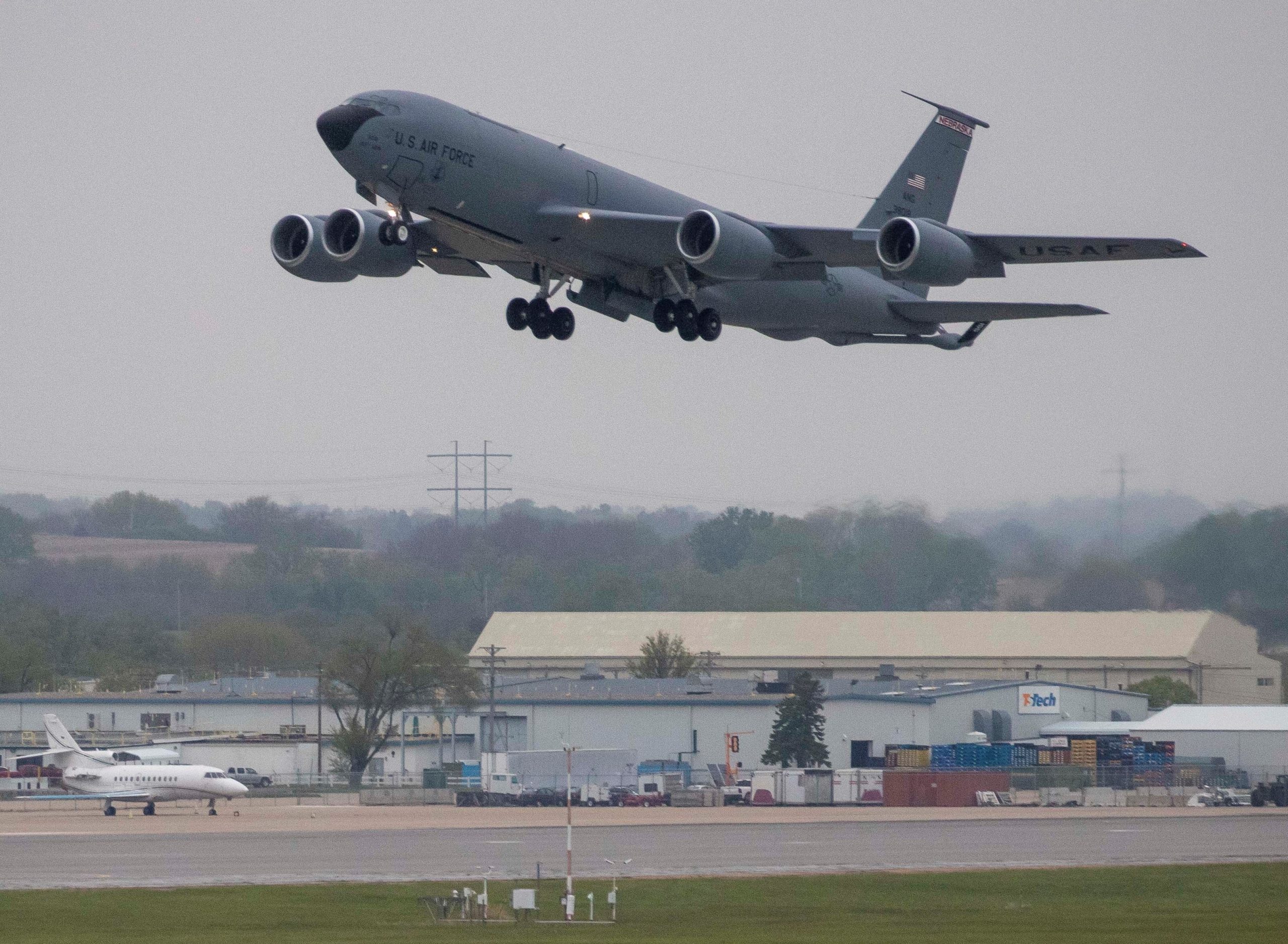


 Reflection of Little Rock Air Force Base C-130J in the windows of a Arkansas hospital, 08MAY2020.
Reflection of Little Rock Air Force Base C-130J in the windows of a Arkansas hospital, 08MAY2020. California Air National Guard’s 115th Airlift Squadron over the Mojave Desert near Palmdale, 14MAY2020.
California Air National Guard’s 115th Airlift Squadron over the Mojave Desert near Palmdale, 14MAY2020.

 403rd Wing’s 815th Airlift Squadron over Mississippi’s Gulf Coast, 28APR2020.
403rd Wing’s 815th Airlift Squadron over Mississippi’s Gulf Coast, 28APR2020.

 New York Air National Guard LC-130 (
New York Air National Guard LC-130 ( A C-130H out of Youngstown Air Reserve Station, Ohio, conducting a second round of pandemic overflights on 07MAY2020. Not only did Ohio aircraft fly over Ohio, but also locations in Pennsylvania.
A C-130H out of Youngstown Air Reserve Station, Ohio, conducting a second round of pandemic overflights on 07MAY2020. Not only did Ohio aircraft fly over Ohio, but also locations in Pennsylvania. Two Ohio Air National Guard 179th Airlift Wing C-130Hs also flew pandemic overflights, 15MAY2020.
Two Ohio Air National Guard 179th Airlift Wing C-130Hs also flew pandemic overflights, 15MAY2020. Naval Air Station Joint Reserve Base Fort Worth, Texas, this Blue Angels C-130 was temporarily brought out of retirement to give moral support, 06MAY2020, unfortunately it was not flown.
Naval Air Station Joint Reserve Base Fort Worth, Texas, this Blue Angels C-130 was temporarily brought out of retirement to give moral support, 06MAY2020, unfortunately it was not flown.
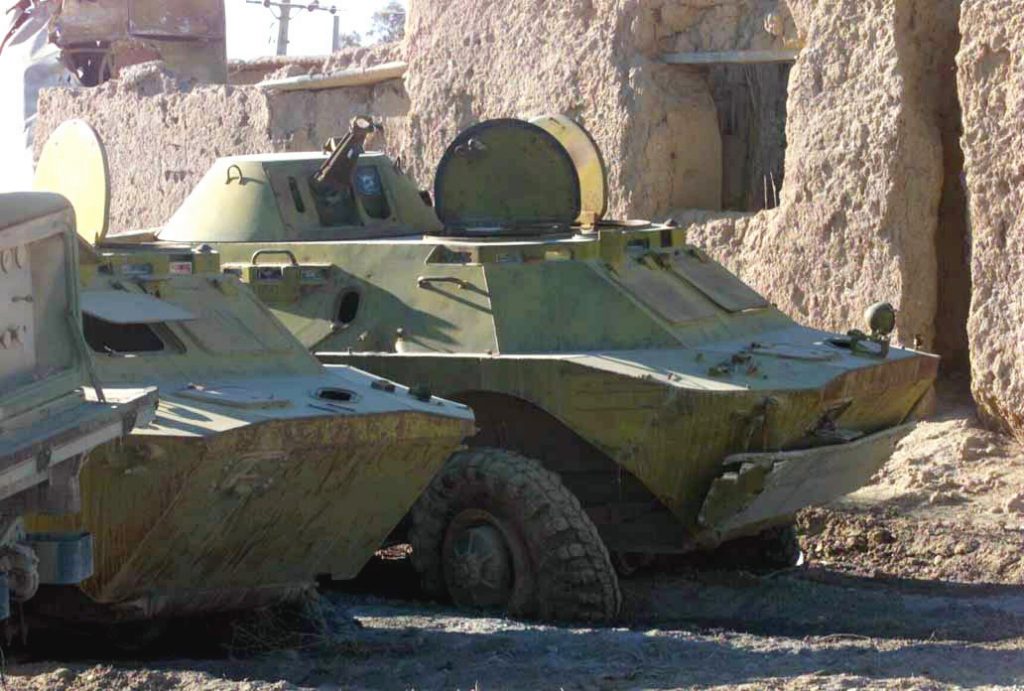
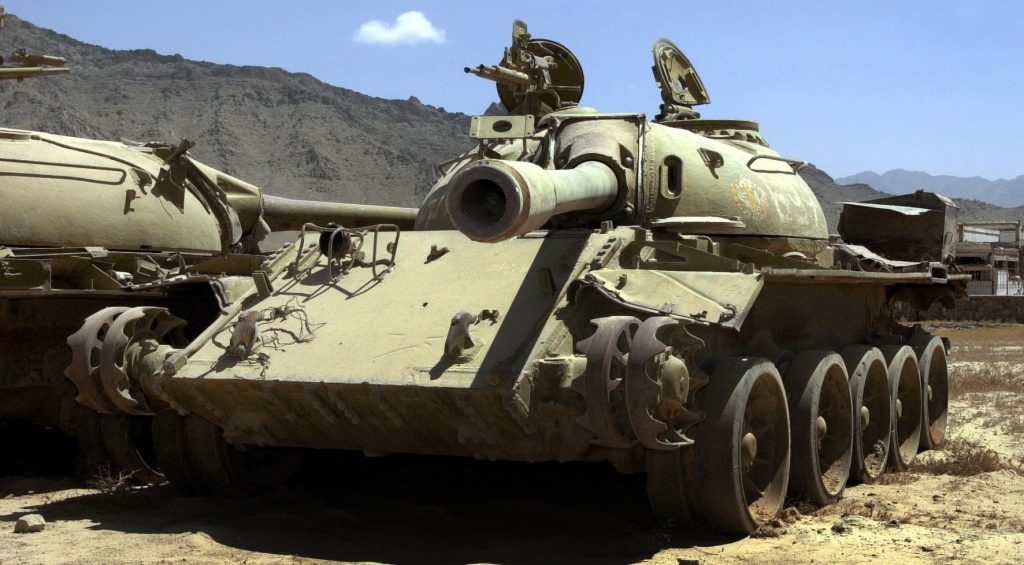
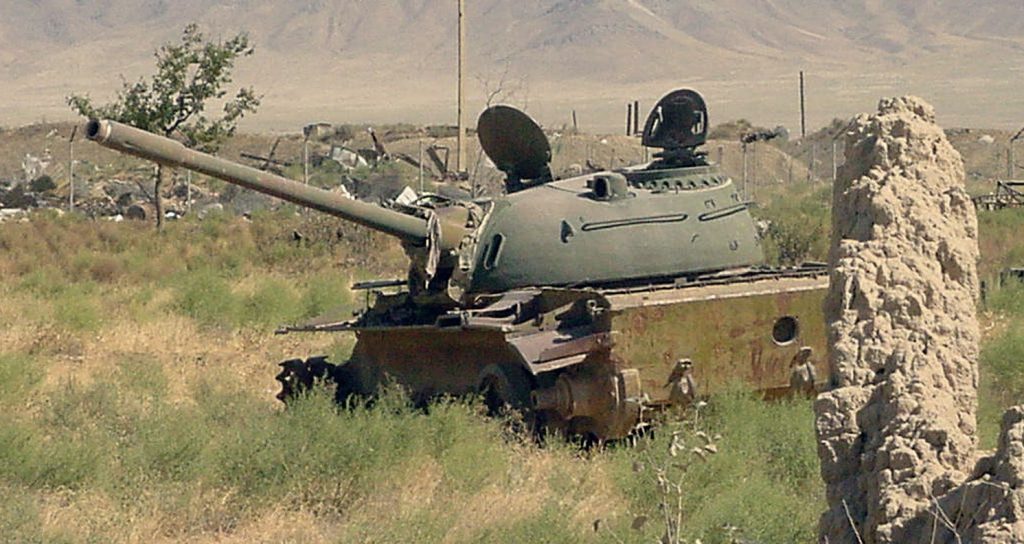
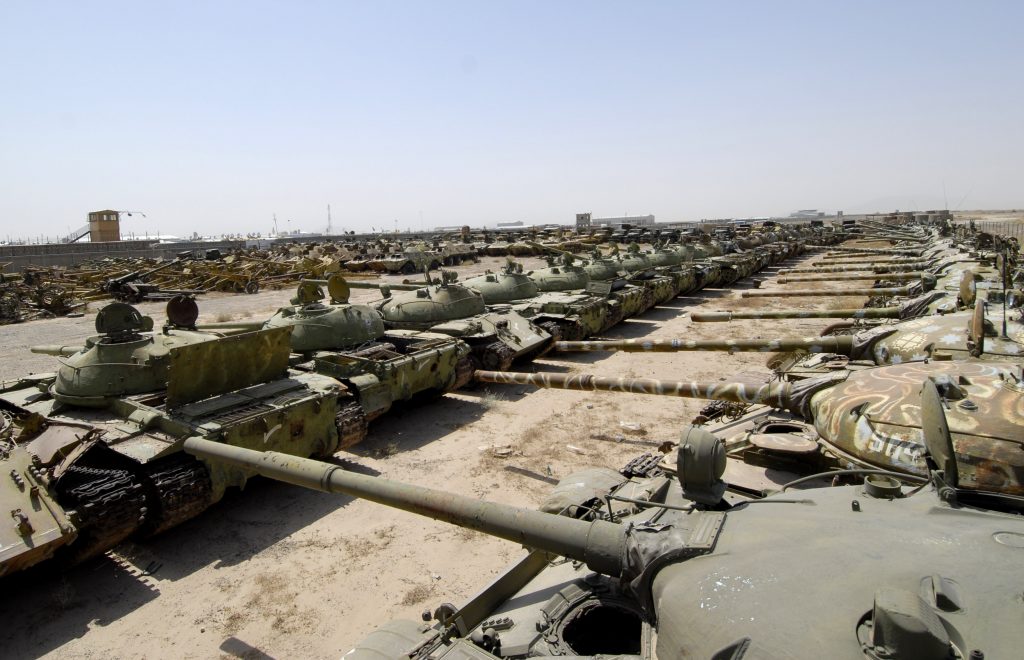
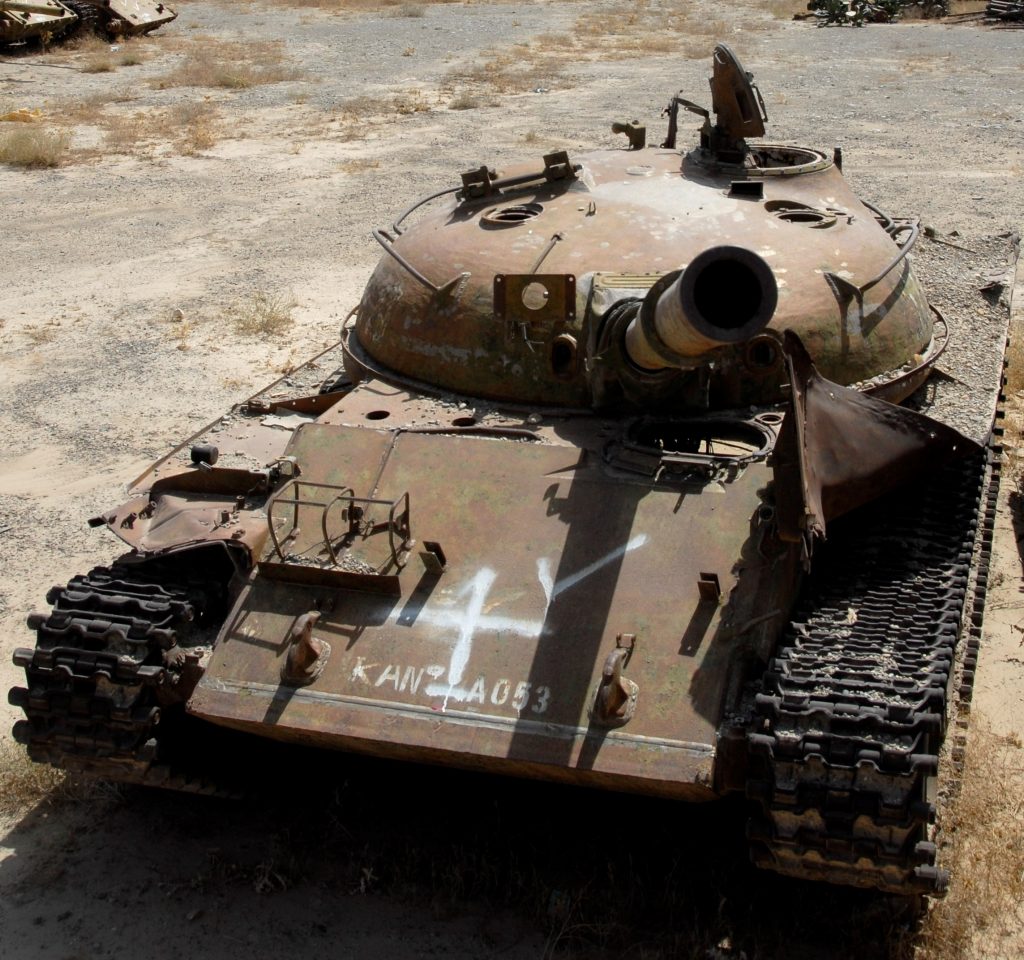
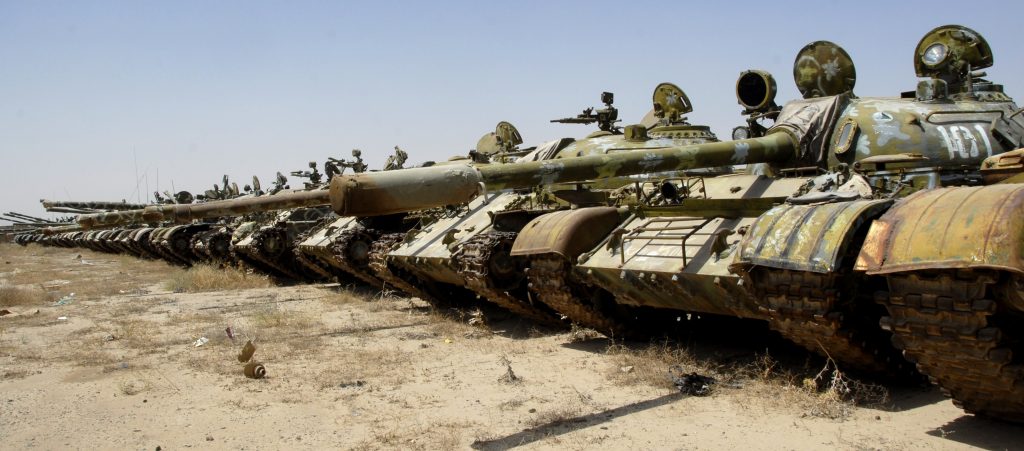
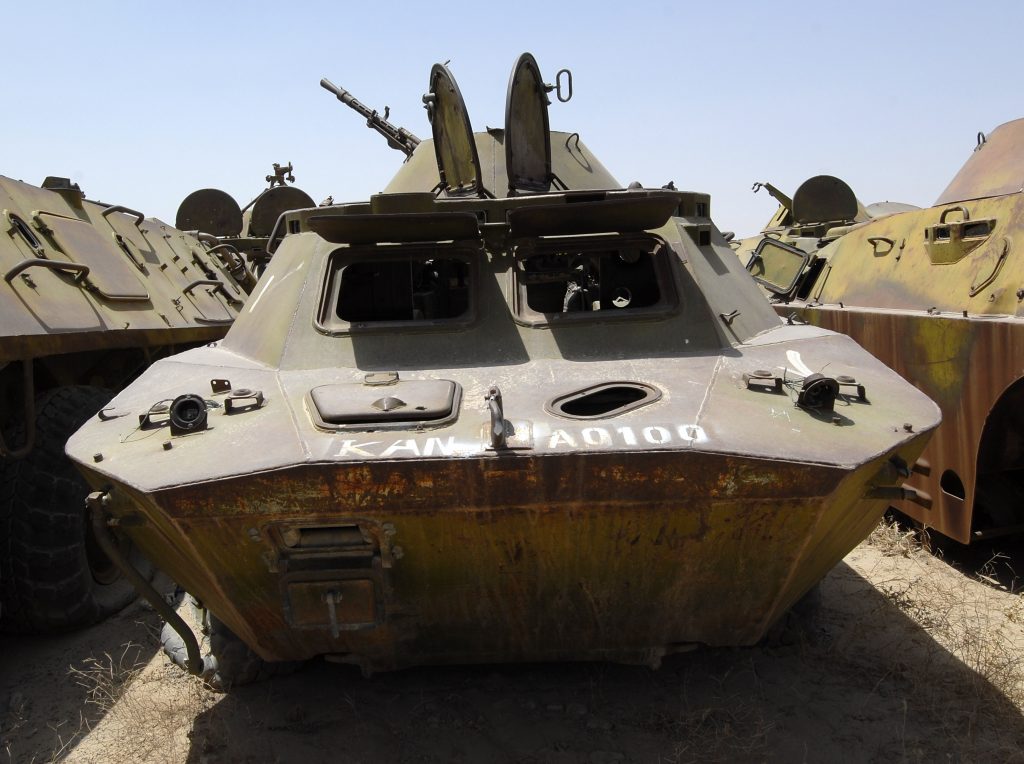
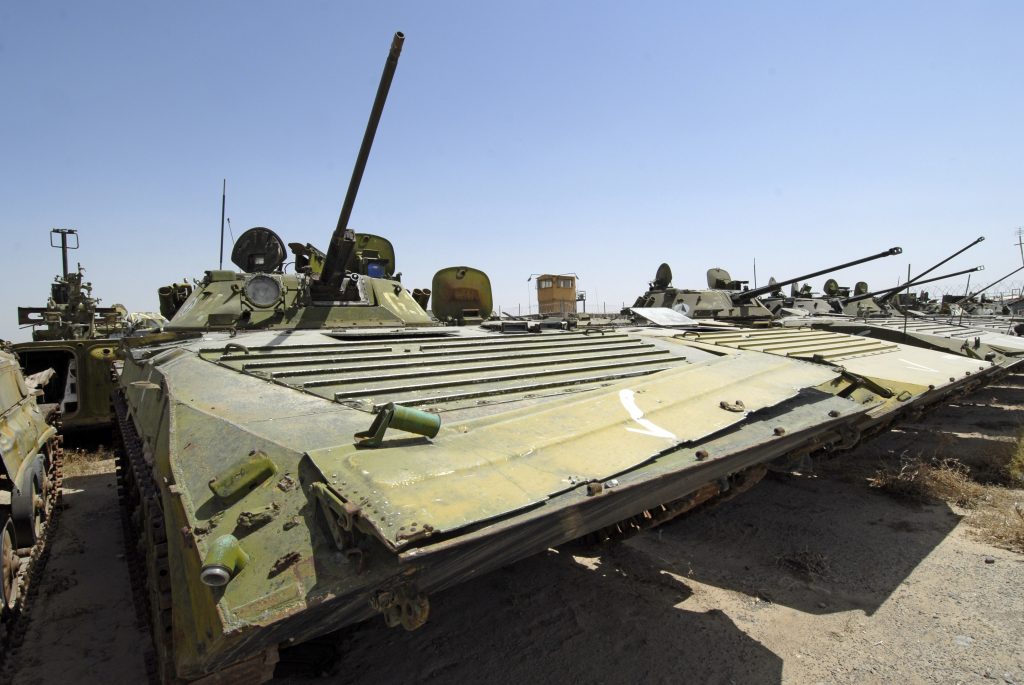





































 Camp Shaheen.
Camp Shaheen. November 2010, a maintenance supervisor with Company D, 186th Brigade Support Battalion, 86th Infantry Brigade Combat Team cuts-up an old Soviet occupation armored vehicle in Durani Village, Parwan Province, Afghanistan. The villagers were able to sell the pieces of steel to recyclers for cash.
November 2010, a maintenance supervisor with Company D, 186th Brigade Support Battalion, 86th Infantry Brigade Combat Team cuts-up an old Soviet occupation armored vehicle in Durani Village, Parwan Province, Afghanistan. The villagers were able to sell the pieces of steel to recyclers for cash. BTR-80, Panjshir Province, Afghanistan, January 2010.
BTR-80, Panjshir Province, Afghanistan, January 2010.
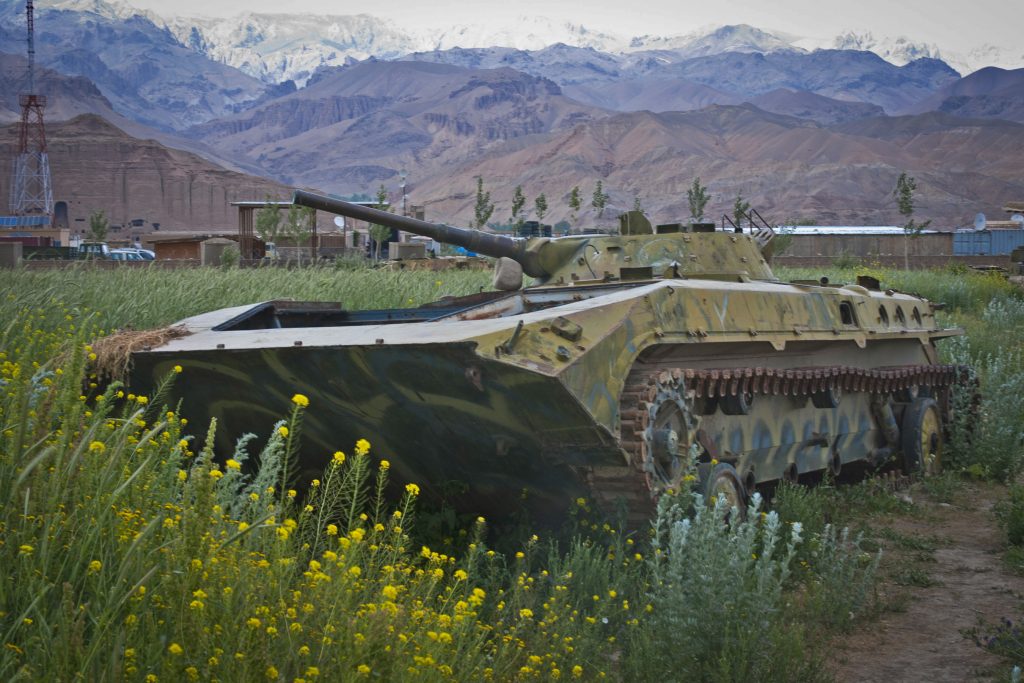



 T-54/55, Bamyan Province.
T-54/55, Bamyan Province. Nowzad, Helmand Province, Afghanistan, February 2011. Children line up for school while a relic (T-55) of the 1980s Soviet occupation rusts away in the background.
Nowzad, Helmand Province, Afghanistan, February 2011. Children line up for school while a relic (T-55) of the 1980s Soviet occupation rusts away in the background. Derelict World War Two era Soviet T-34/85 in Muqer District, Ghazni Province, March 2012.
Derelict World War Two era Soviet T-34/85 in Muqer District, Ghazni Province, March 2012. T-55 in Nowzad, Helmand Province, Afghanistan February 2012.
T-55 in Nowzad, Helmand Province, Afghanistan February 2012. Remains of ZSU-23-4, Bala Hissar Fortress, August 2013. You can see where the anti-aircraft tank took a direct hit in the side.
Remains of ZSU-23-4, Bala Hissar Fortress, August 2013. You can see where the anti-aircraft tank took a direct hit in the side.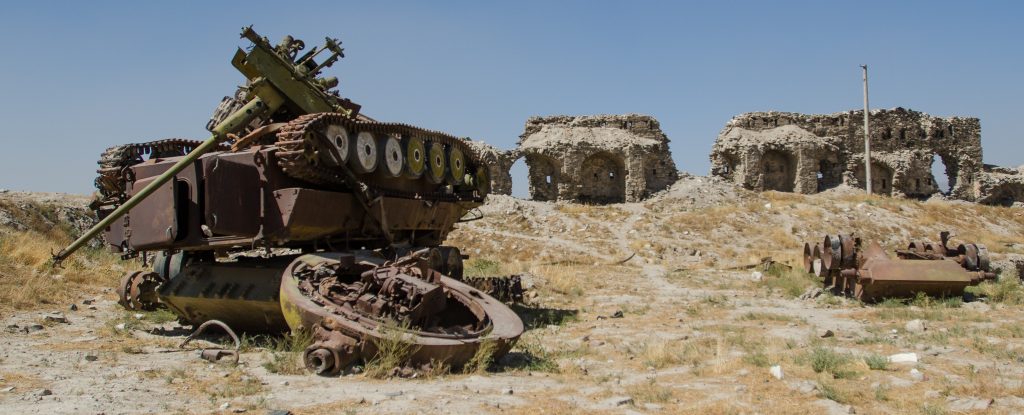
 BMP-1s and a T-54/55 (without bore evacuator) in Bamyan Province, February 2013.
BMP-1s and a T-54/55 (without bore evacuator) in Bamyan Province, February 2013. Soviet occupation era T-55 still in use. The U.S. Marine Corps observed Afghan government forces use it against rebel troops in Sangin District, Helmand Province, August 2018.
Soviet occupation era T-55 still in use. The U.S. Marine Corps observed Afghan government forces use it against rebel troops in Sangin District, Helmand Province, August 2018.